Being pregnant with an infected partner can be a daunting and worrisome experience. With the risks of transmitting the infection to your unborn child, it is important to understand the potential risks and take steps to ensure the safety of you and your baby. In this article, we will explore the risk factors associated with being pregnant with an infected partner, discuss ways to reduce the risk of transmission, and provide tips for managing the situation. By understanding the risks involved, you can make informed decisions about your own health and that of your unborn child. Being pregnant while your partner has an active herpes infection can be a scary situation.
It is important to understand the risks and know how to protect yourself during pregnancy. The first step is to understand the risks associated with being pregnant while your partner has an active herpes infection. Herpes is a virus that is spread through contact, so it is possible for the virus to be transmitted from the infected partner to the pregnant woman. This can lead to serious complications for both the mother and baby, such as miscarriage, preterm labor, stillbirth, and newborn death.
It is important to talk to your healthcare provider if you think you may have been exposed to the virus, as they can provide testing and treatment options. Next, it is important to learn how to protect yourself during pregnancy. Herpes can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, so it is important to practice safe sex by using condoms. Additionally, it is important for both partners to be tested for the virus, even if there are no visible symptoms. This will help ensure that both partners are aware of their status and can take the necessary precautions. It is also important to know how to manage any symptoms that may arise during pregnancy.
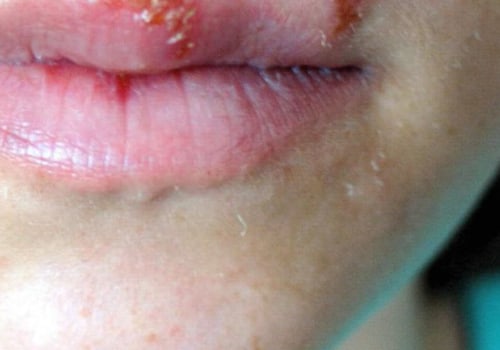
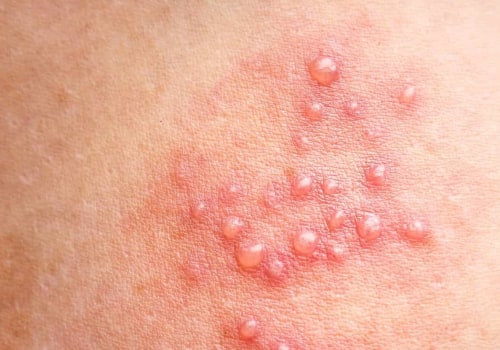
These can include fever, swollen glands, and sores or blisters on or around the genitals or mouth. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, as antiviral medication may be needed in order to reduce the risk of transmission to the baby. Lastly, it is important to understand that there are some steps that can be taken in order to reduce the risk of transmission. These include avoiding sexual contact when either partner has symptoms, avoiding touching sores or blisters on the skin, and washing hands after touching any areas that may have been exposed. Additionally, it is important for both partners to be tested for herpes before engaging in any sexual activity during pregnancy.
Reducing Transmission Risk
It is possible to reduce the risk of transmission from an infected partner when a woman is pregnant.The following steps can help reduce the risk:Practicing safe sexUsing condoms and other barrier protection during sexual intercourse can help to prevent the spread of herpes. It is important to avoid any contact with the infected partner's genital area if there are signs of active herpes lesions.
Avoiding sexual intercourse during outbreaks
If the infected partner has an active herpes outbreak, it is best to avoid sexual intercourse until the outbreak has resolved. This will help prevent the spread of the virus.Managing stress levels
Stress can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. It is important to practice stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise to help keep stress levels under control.Eating a healthy diet
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-dense foods can help boost the immune system and make it easier for the body to fight off infections.It is also important to limit processed foods and refined sugars as these can weaken the immune system. It is also important to limit processed foods and refined sugars as these can weaken the immune system.
Risks Associated with Being Pregnant with an Infected Partner
When a pregnant woman is exposed to an active herpes infection, there is a risk of transmitting the virus to the unborn baby. This can result in a range of complications, including birth defects, brain damage, blindness, and even death. The virus can also be passed from mother to child during delivery, increasing the risk of neonatal herpes. Other risks associated with being pregnant with an infected partner include increased risk of miscarriage or stillbirth, preterm labor, and low birth weight.These risks may be higher if the pregnant woman has her own active infection. Pregnant women should also be aware of the potential for developing genital herpes during pregnancy, as the virus can be transmitted to the baby through a vaginal birth. It is important to talk to a doctor if you think you may have been exposed to an active herpes infection. Your doctor can discuss treatment options that may reduce the risk of passing the virus to your baby.
Protecting Yourself During Pregnancy
When you are pregnant and your partner has an active herpes infection, it is important to take steps to protect yourself. The risk of passing the virus to the baby is greatest during the first trimester, so you should take extra precautions to ensure your safety. The first step is to talk to your healthcare provider about the risks associated with your partner's herpes.They can provide advice on how to protect yourself and what treatments might be available. Additionally, your partner should also talk to their healthcare provider about their infection, so that they can be aware of any risks as well. You should also practice safe sex during pregnancy. This means using condoms, dental dams, or other forms of protection every time you have sexual contact. This will help reduce the risk of transmission. It is also important to avoid sharing items such as towels or razors with your partner.
This is because the virus can be spread through direct contact with the infected area. If you must share items with your partner, make sure they are properly washed or disinfected first. Finally, if your partner experiences any symptoms of a herpes outbreak (such as itching, burning, or blisters), they should refrain from having any sexual contact until they are symptom-free. This will help reduce the risk of transmission.
Managing Symptoms During Pregnancy
When a pregnant woman's partner has an active herpes infection, it is important to know how to manage the symptoms that may arise during pregnancy. If the woman has an active herpes infection, she may experience symptoms such as sores, itching, or burning in the genital area.It is important to monitor these symptoms and seek medical attention if necessary. Additionally, it is important for pregnant women to practice safe sex and avoid skin-to-skin contact with the infected partner to prevent transmission of the virus. If a pregnant woman does experience active symptoms of herpes, her doctor may prescribe antiviral medications to help reduce the severity of the outbreak and reduce the risk of transmission to the baby. Additionally, pain medications can be used to help relieve any discomfort associated with the outbreak. It is important to discuss any medications with a doctor before taking them during pregnancy. It is also important for pregnant women to follow a healthy lifestyle.
Eating a balanced diet, getting plenty of rest, and avoiding stress can all help to reduce symptoms of herpes and promote overall health. Additionally, it is important to practice safe sex and not engage in sexual activities with anyone who has an active infection. By understanding the risks associated with being pregnant with an infected partner and taking steps to protect yourself, you can reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy. It is important to speak with your doctor about any concerns you may have about herpes and your pregnancy. Being pregnant while your partner has an active herpes infection can be a scary situation. Talk to your healthcare provider if you think you may have been exposed and practice safe sex by using condoms.
Taking precautionary steps such as these can help reduce the risk of transmitting the virus during pregnancy. It is important to remember that while being pregnant with an infected partner can be a cause for concern, there are ways to manage the situation and reduce the risk of transmission. Understanding the risks associated with being pregnant with an infected partner, protecting yourself during pregnancy, managing symptoms during pregnancy, and reducing transmission risk are all key components to a healthy and safe pregnancy.