Genital herpes is asexually transmitted infection that can be both physically and emotionallypainful. It's estimated that more than one in six people aged 14 to 49 havegenital herpes, making it one of the most common sexually transmittedinfections (STIs). Thankfully, modern medicine has developed numerous tests fordiagnosing genital herpes. Today, we'll explore viral culture tests and theirimportance in diagnosing this infectious disease. With a creative hook likethis, you may find yourself asking: What exactly are viral culture tests andhow do they help diagnose genital herpes? Read on to find out!
Definition of GenitalHerpes
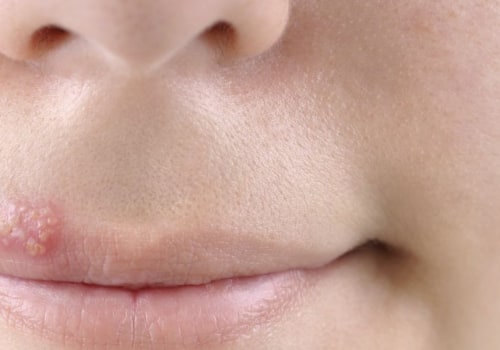
Genital herpes is asexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more thanone in six people aged 14 to 49 have genital herpes. It can be spread throughsexual contact with someone who has an HSV infection, even if they don’t showany symptoms.
The main symptom ofgenital herpes is genital lesions, which may appear as blisters or sores on thegenitals and rectum. Other symptoms may include itching, burning, pain duringurination, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. In somecases, the person infected may experience no signs or symptoms at all.
If you believe you mayhave been exposed to HSV or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it'simportant to get tested right away. Diagnosing genital herpes typicallyinvolves taking a sample from affected tissue and performing either a viralculture test or a blood test. Viral culture tests are used to confirm thepresence of HSV while blood tests detect type-specific antibodies produced inresponse to an HSV infection.
It's important to takethe necessary steps if you think you may have been exposed to HSV andunderstand the symptoms of genital herpes. The next section will explore whatto look out for and how to best stay informed.
Symptoms of GenitalHerpes
Genital herpes is asexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Ittypically presents with genital lesions such as blisters or sores, but somepeople may experience no signs or symptoms at all. Other common symptomsinclude itching, burning, and pain during urination, as well as flu-likesymptoms such as fever and swollen lymph nodes. Identifying the presence of HSVis important in order to help prevent its spread to sexual partners. Diagnosistypically involves taking a sample from affected tissue and performing either aviral culture test or a blood test. If you think you may have been exposed toHSV, it's important to get tested right away in order to take appropriateaction.
Overview of ViralCulture Tests for Diagnosing Genital Herpes
Viral culture tests arecommonly used to diagnose genital herpes, a sexually transmitted infectioncaused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). In this test, a sample of affectedtissue is taken and placed in a special media that encourages viral growth. IfHSV is present, it will typically multiply within two to three days, formingvisible colonies known as plaques. To confirm the diagnosis, a doctor mayexamine these plaques under a microscope and look for the presence of giantcells — an indication of HSV infection. Viral culture tests can also be used todetermine which type of HSV infection is present: either HSV-1 (which typicallycauses cold sores) or HSV-2 (which primarily causes genital herpes). TheCenters for Disease Control and Prevention recommend viral culture tests fordiagnosing symptomatic genital herpes infections. However, for people who haveno signs or symptoms but may have been exposed to HSV through sexual contact oractivity, blood tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or type-specificantibodies testing are recommended.
Types of Herpes SimplexVirus (HSV)
Herpes simplex virus(HSV) is a type of virus that can cause several types of infections. The twomain types of HSV are herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and herpes simplexvirus type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 is typically associated with oral herpes, whichcauses cold sores and fever blisters around the mouth. While HSV-2 primarilycauses genital herpes, it can also cause oral herpes in some cases. Genitalherpes is usually transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person,such as through vaginal, anal or oral intercourse. Symptoms of genital herpesmay include painful genital lesions, genital ulcers and itching or burningsensations in the genitals. In some cases, people may not experience anysymptoms at all but can still transmit the infection to their sexual partners.Early detection and diagnosis of HSV infections is essential in order to reducethe risk of complications and spread to other people.
Overall, HSV is a virusthat can cause serious infections and has the potential to spread easily fromone person to another. It is important for people to understand the risksassociated with this virus and take steps to protect themselves againstinfection. So be sure to stay informed about HSV-1 and HSV-2 and how they canaffect your health! And in our next section, we'll look at some of the keydifferences between these two types of herpes simplex viruses.
HSV-1 and HSV-2
Herpes Simplex Virus(HSV) is a type of virus that can cause several types of infections, includingoral herpes and genital herpes. HSV-1 is typically associated with oral herpes,which causes cold sores and fever blisters around the mouth. Whereas HSV-2primarily causes genital herpes, it can also cause oral herpes in some cases.It is important to be aware of the differences between these two types ofviruses in order to prevent, diagnose and treat infections properly and reducetheir spread to others.
HSV-1 is more easilyspread through skin contact or saliva than HSV-2, which is mainly transmittedthrough sexual contact. Symptoms of HSV-1 may include cold sores or feverblisters around the mouth while symptoms of HSV-2 may include painful genitallesions, genital ulcers and itching or burning sensations in the genitals.Early detection and diagnosis of both types of HSV infections are essential forreducing the risk of complications as well as transmission to other people.
Fortunately, there are avariety of diagnostic tests available for diagnosing both types of HSV, such asviral culture tests, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests and type-specificantibody tests. These tests can help detect the presence of the virusaccurately so that proper treatment can be administered promptly to reducesymptoms and further spread.
Giant Cells
Giant cells are large,multinucleated cells that can be found in the body and are associated withvarious viral infections. They are typically seen in conditions like herpessimplex virus (HSV) infections, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections, rubella virusinfections and other viral illnesses. Giant cells form when multiple nuclei ofsmall lymphocytes join together to form a single giant cell. In the presence ofHSV-2 or another virus, these giant cells will often appear as clusters orplaques on the surface of infected tissues and can be seen under a microscopeduring laboratory tests.
Giant cells are animportant indicator for diagnosing HSV-2 or other genital herpes simplex virusinfections because they can provide evidence of an active infection. Inaddition, giant cells help confirm the presence of herpes simplex virus incases where there is already evidence of a type-specific antibody response bythe immune system. Therefore, if giant cells are present in a sample taken fromsomeone with genital ulcer disease, this suggests that they have been infectedwith HSV-2 or another genital herpes virus.
Centers for DiseaseControl and Prevention (CDC) Guidelines for Diagnosing Genital Herpes
The Centers for DiseaseControl and Prevention (CDC) recommends that healthcare providers use acombination of diagnostic tests to diagnose genital herpes. The most commonlyused tests include viral culture, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), andtype-specific antibodies.
Viral culture is thetraditional method for diagnosing genital herpes. A swab from an active lesionor fluid from a blister is taken and cultured in the laboratory to look for thepresence of HSV-2 or another herpes simplex virus.
PCR is a newer test whichidentifies the genetic material of HSV-2 in samples taken from active lesionsand can detect even small amounts of virus. PCR testing is generally moreaccurate than viral culture but it is more expensive and may not be availableat all laboratories.
Type-specific antibodytests are blood tests that measure specific antibodies against HSV-2 or othertypes of herpes simplex virus. These tests can be used to distinguish betweencurrent infections, past infections, or both, depending on the quality of thetest used.
The CDC also recommendsthat healthcare providers counsel patients about how to reduce their risk oftransmitting genital herpes to sex partners by informing them about limitingsexual contact during outbreaks and taking antiviral medications as prescribed.It also advises patients to inform all current and future sexual partners abouttheir diagnosis so they can take precautions as well.
It is important torecognize the importance of diagnosis, prevention and management of genitalherpes. By utilizing a combination of diagnostic tests and following CDCrecommendations for managing infection, we can reduce the risk of transmissionand improve overall health outcomes. Get ready to learn more about the CDC'srecommendations on diagnostic testing for genital lesions in the next section!
CDC Recommendations onDiagnostic Testing for Genital Lesions
The Centers for DiseaseControl and Prevention (CDC) recommends a combination of diagnostic tests toconfirm the diagnosis of genital herpes. The most commonly used tests are viralculture, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and type-specific antibodies. Viralculture is the traditional method for diagnosing genital herpes, in which aswab from an active lesion or fluid from a blister is taken and cultured in thelaboratory to look for the presence of HSV-2 or another herpes simplex virus.PCR testing is generally more accurate than viral culture but more expensiveand may not be available at all laboratories. Type-specific antibody testsmeasure specific antibodies against HSV-2 or other types of herpes simplexvirus. These tests can help distinguish between current infections, pastinfections, or both, depending on the quality of the test used. It is importantto recognize that proper diagnosis and management of genital herpes isessential to reduce transmission risk and improve overall health outcomes.
General Procedures forDiagnosing Genital Herpes Through Viral Culture Tests
Viral culture tests are acommon and reliable method for diagnosing genital herpes. The procedureinvolves taking a swab from an active lesion or fluid from a blister andculturing it in the laboratory to detect the presence of herpes simplex virus(HSV). For optimal accuracy, specimens are usually collected between 48-72hours after symptoms first appear. The specimen may be sent to a laboratory foranalysis, where it is grown in a cell culture and examined under the microscopeto look for giant cells, which indicate HSV infection. A positive resultindicates that HSV is present, while a negative result does not rule out HSV infectionand should be followed up with other tests such as blood tests or type-specificantibody testing. Viral culture tests can help confirm current or ongoinginfections and may be used in conjunction with other tests to accuratelydiagnose genital herpes in individuals who have had sexual contact with aninfected person or those who have experienced signs and symptoms consistentwith genital herpes simplex virus infection.
Viral culture tests offera reliable and accurate way to diagnose genital herpes and should be used inconjunction with other tests to ensure an accurate result. Now, let's take acloser look at the specimen collection and examination process for this test.
Specimen Collection andExamination Process
Specimen collection andexamination for viral culture tests is a relatively simple process. First, themedical practitioner will take a swab or fluid sample from an active lesion orblister on the genital area. The sample is then sent to a laboratory foranalysis, where it is grown in a cell culture and examined under the microscopeto look for giant cells, which indicate HSV infection. The results of the testare usually available within 2-3 days and are usually accurate if taken within48-72 hours of symptom onset. Additionally, the specimen may be tested forother sexually transmitted infections or diseases such as HIV or syphilis,depending on case history and risk factors. It is important to note that evenif the test results come back negative, this does not rule out HSV infection. Furthertesting with blood tests or type-specific antibody testing may be necessary inorder to accurately diagnose genital herpes in individuals who have had sexualcontact with an infected person or those who have experienced signs andsymptoms consistent with genital herpes simplex virus infection. Specimen collection andexamination for viral culture tests is a relatively simple process. First, themedical practitioner will take a swab or fluid sample from an active lesion orblister on the genital area. The sample is then sent to a laboratory foranalysis, where it is grown in a cell culture and examined under the microscopeto look for giant cells, which indicate HSV infection. The results of the testare usually available within 2-3 days and are usually accurate if taken within48-72 hours of symptom onset. Additionally, the specimen may be tested forother sexually transmitted infections or diseases such as HIV or syphilis,depending on case history and risk factors. It is important to note that evenif the test results come back negative, this does not rule out HSV infection. Furthertesting with blood tests or type-specific antibody testing may be necessary inorder to accurately diagnose genital herpes in individuals who have had sexualcontact with an infected person or those who have experienced signs andsymptoms consistent with genital herpes simplex virus infection.
Collection Media Used toCultivate the Sample in a Lab Setting
Collection media is atype of liquid that is used in a laboratory setting to cultivate a sample froman individual. This liquid helps the specimen grow in cell culture, and is alsoused to detect giant cells which indicate HSV infection. Collection mediatypically contain proteins, carbohydrates, and other nutrients that arenecessary for the growth of viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Depending on the needsof the lab technician, these collection media can be customized to adjust pHlevels, osmolarity levels, or other factors specific to the specimen beingtested. Collection media can also contain antibiotics which inhibit anypotential bacterial contamination of the sample while it is cultured in vitro(outside of its natural environment). It is important for laboratories to usesterile collection media so as not to introduce any unwanted contaminants intothe sample during processing.
Different Steps Involvedin the Culturing Process
The culturing process isan important step in the diagnosis of genital herpes. It involves taking asample of fluid or tissue from the affected area and culturing it in alaboratory setting. This process begins with obtaining a specimen, which can bedone through swabbing an active lesion or taking a blood sample. Once obtained,the specimen must then be prepared for testing by adding collection media toensure ideal conditions for growth. The specimen is then placed into an appropriatecontainer and incubated at 37°C until results are obtained. After incubation,the specimen is examined under the microscope to look for evidence of viralinfection. If present, a positive result is reported and further testing suchas PCR or type-specific antibody testing may be recommended to confirm thediagnosis. Culturing is an effective tool for diagnosing genital herpes becauseit allows for accurate detection of HSV infections even when no symptoms arepresent. The culturing process isan important step in the diagnosis of genital herpes. It involves taking asample of fluid or tissue from the affected area and culturing it in alaboratory setting. This process begins with obtaining a specimen, which can bedone through swabbing an active lesion or taking a blood sample. Once obtained,the specimen must then be prepared for testing by adding collection media toensure ideal conditions for growth. The specimen is then placed into an appropriatecontainer and incubated at 37°C until results are obtained. After incubation,the specimen is examined under the microscope to look for evidence of viralinfection. If present, a positive result is reported and further testing suchas PCR or type-specific antibody testing may be recommended to confirm thediagnosis. Culturing is an effective tool for diagnosing genital herpes becauseit allows for accurate detection of HSV infections even when no symptoms arepresent.
Commonly Used Tests toDiagnose Genital Herpes Through Viral Culture Tests
Viral culture tests arecommonly used to diagnose genital herpes. This test is conducted by obtaining asample from the affected area and culturing it in a laboratory setting. Thecollected specimen is then added to collection media for optimal growthconditions and incubated at 37°C until results can be obtained. Uponexamination, if the virus is present, it will appear as giant cells or herpesvirus under the microscope. A positive result indicates that the patient has anactive herpes infection and further tests may be recommended in order toconfirm this diagnosis. Blood tests such as type-specific antibodies orpolymerase chain reaction (PCR) may also be used to detect HSV infections inpatients who have had recent sexual contact or activity with someone infectedwith herpes simplex virus infections. Centers for Disease Control andPrevention (CDC) recommends that all sexual partners of a person diagnosed withgenital herpes get tested for the infection even if they do not show anysymptoms.
Genital herpes infectionscan have a significant impact on patients’ physical and mental health, so it isimportant to get tested if you think you may have been exposed. For those whoare already diagnosed, proper management of the infection is key to reducingits symptoms and minimizing the risk of transmitting it to others. Next up,we'll take a look at the Prober CG Test – an alternative method for detectingherpes simplex virus infections.
Prober CG Test
The Prober CG Test is analternative method of detecting HSV infections. It involves the use of a swabto take samples from the affected area, which are then tested for the presenceof herpes simplex virus antigens. This test is easier and faster than viralculture tests, as results can be obtained in minutes, compared to several dayswith traditional testing methods. Moreover, it does not require any specialequipment or laboratory setting as samples can be analyzed with handhelddevices. Additionally, it has been found to be more accurate in cases ofgenital herpes where there may not be any visible lesions present. As such,this test is ideal for those who want quick and reliable results without havingto wait days or weeks for a diagnosis.
Polymerase ChainReaction (PCR) Test
PCR testing is a highlysensitive and specific technique used to diagnose HSV infections. It involvestaking a sample of the affected area, either through swabbing or blood tests,and then amplifying the genetic material of the virus so that it can beidentified. This method is preferred over traditional methods such as viralculture tests due to its accuracy and speed; results can be obtained in just afew days compared to weeks with other methods. Additionally, PCR testing ismore effective than antibody-based blood tests, which can take several weeks todetect an infection. This test is also ideal for those who may not display anyvisible signs or symptoms of herpes since it detects even low levels of thevirus and can provide results quickly.
Type-Specific AntibodiesTest
The Type-SpecificAntibodies Test is a reliable and accurate method used to diagnose herpessimplex virus (HSV) infections. This test works by detecting the presence oftype-specific antibodies, which are produced by the body’s immune system inresponse to an HSV infection. A sample of blood is drawn from the patient andanalyzed for the presence of these antibodies, which can indicate a current orpast infection. The results of this test can provide valuable information aboutthe type of HSV infection present and whether it is active or inactive. Thistype of testing is especially important for those who have recently beenexposed to genital herpes or have had sexual contact with someone who has HSV,as it can help detect any potential infections early on. It can also bebeneficial for individuals at risk for recurrent outbreaks as this test canhelp identify whether they need to take preventive measures such as antiviralmedications.
Advantages andDisadvantages of Using Viral Culture Tests to Diagnose Genital Herpes
Viral culture tests are acommon diagnostic test used to detect genital herpes. This test involves takinga sample from the affected area and culturing it in the laboratory. The resultsof this test can be beneficial in helping to diagnose genital herpes, as wellas provide insight into how severe the infection is.
Advantages of using viralcultures include that they are widely available, relatively inexpensive, andeffective for detecting herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections. They are alsohighly accurate and allow for rapid diagnosis within a few days or even hours,depending on the type of testing used. Additionally, this method providesinformation about the type of HSV present (HSV-1 or HSV-2), which can help guidetreatment options.
Disadvantages of viralculture testing include that it is not always reliable due to potentialfalse-negative results and difficulty in obtaining accurate samples fromgenital lesions or ulcers. In addition, centers for disease control andprevention (CDC) guidelines do not recommend this method for screening sexualpartners who may have been exposed to HSV infection due to its limitedsensitivity. Furthermore, patients with recurrent outbreaks may require repeattesting over time to monitor the progress of their condition.
Overall, viral culturetests can be an effective tool for diagnosing genital herpes in individualswith active lesions or ulcers. However, it is important to weigh the advantagesand disadvantages when making decisions about testing methods since there areother diagnostic tools such as blood tests or polymerase chain reaction (PCR)tests available that may be more suitable in certain cases.
In conclusion, viralculture testing is a reliable and cost-effective method for diagnosing genitalherpes. However, it is important to understand its advantages and disadvantagesin order to make the most informed decision possible. Stay tuned to learn moreabout the pros and cons of this diagnostic test!
Advantages Disadvantages
Viral culture tests arean effective and widely available diagnostic option for identifying genitalherpes infections. They are relatively inexpensive, highly accurate, andprovide rapid results within a few days or even hours. Additionally, thismethod can also indicate the type of HSV present (HSV-1 or HSV-2), which canhelp guide treatment options. However, there are some disadvantages to usingviral culture tests for diagnosing genital herpes. These include potentialfalse-negative results due to difficulty in obtaining accurate samples fromgenital lesions or ulcers; CDC guidelines may not recommend this method forscreening sexual partners; and patients with recurrent outbreaks may requirerepeat testing over time to monitor the progress of their condition. It isimportant to consider both the advantages and disadvantages when makingdecisions about testing methods as other diagnostic tools such as blood testsor polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests may be more suitable in certain cases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, viralculture tests are a reliable and cost-effective way to diagnose genital herpesinfections. This method is relatively quick and can indicate which type of HSVis present. However, there are some disadvantages to this method that must betaken into account, such as potential false-negative results or the need forrepeat testing in recurrent cases. Ultimately, it is important to consider boththe advantages and disadvantages when determining which diagnostic test is bestfor each individual case.